Your Gateway to Spatial Solutions
Call/WhatsApp +92 345 2997342
Satellites use diverse wavelengths to reveal unseen wonders. Multispectral/hyperspectral imagery provides valuable insights for vegetation, minerals, and more.

Satellites play a crucial role in expanding our vision and revealing unseen wonders. By capturing imagery in various wavelengths, including red, green, blue, near-infrared, shortwave infrared, and hyperspectral ranges, satellites enable us to “see” what would otherwise remain invisible to us.
Through spectral analysis, we delve into the diverse wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum, ranging from blue (~400 μm) to near-, mid-, and long-range infrared. Each wavelength tells a unique story, providing valuable insights into man-made materials, rock types, minerals, plant species, and much more. These types of imagery, known as multispectral and/or hyperspectral imagery, contain multiple spectral bands, forming a rich tapestry of information.
The more bands we have, the more solutions and answers we can uncover. By venturing beyond the visual perspective and exploring the NIR, SWIR, and TIR bands, we gain access to the hidden spectra of the data. This opens up exciting possibilities, such as species of vegetation identification, mineral mapping, and disturbance monitoring.
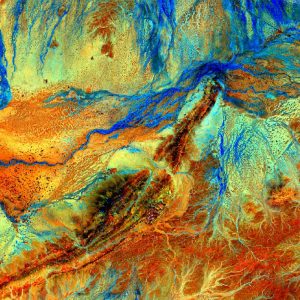
At Geoimage, we offer off-the-shelf spectral packages designed to help you find answers without the hassle of processing the raw data. Here are some of our featured packages.
Geological interpretation: Gain insights into geological features and formations using advanced spectral analysis techniques.
Invasive species/weed detection and monitoring: Identify and monitor the spread of invasive species or weeds for effective management.
Mangrove classification: Analyse mangrove habitats and track changes in their distribution for conservation purposes.
Methane detection: Detect and monitor methane emissions for environmental and industrial applications.
Lithium detection: Assess lithium deposits and potential mining sites using specialised spectral analysis.
Urban heat mapping: Analyse the heat distribution in urban areas to optimise energy consumption and urban planning.
Disturbance monitoring: Monitor and assess the impact of disturbances, such as deforestation or land development, on ecosystems.
Gas leak detection and monitoring: Identify and monitor gas leaks in industrial settings for safety and environmental compliance.
Algae bloom detection and monitoring: Identify and track algal blooms to protect aquatic ecosystems and water quality.
Flood mapping: Create accurate flood maps to support disaster management and mitigation efforts.
Image ProcessingMost types of raw satellite imagery require some type of geometric correction or rectification so that the image corresponds to real-world
Satellite ImagerySatellite imagery is essential for monitoring human activities and natural processes globally.ER Solutions provides enhanced data through satellite partnerships to cater